The International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) develops Incoterms, which are a set of standard contract terms that help define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. First published by ICC in 1936, Incoterms® rules are a set of eleven three-letter trade terms, reflecting business-to-business practice in contracts for the sale and purchase of goods.
Purpose: Incoterms help clarify the tasks, costs, and risks involved in the delivery of goods. They are recognized by UNCITRAL as the global standard for interpreting the most common terms in foreign trade.
Rules: ICC Incoterms rules help to avoid costly misunderstandings by clarifying the tasks, costs and risks involved in the delivery of goods from sellers to buyers. The most recent version of Incoterms is Incoterms 2020, which entered into force on January 1, 2020.
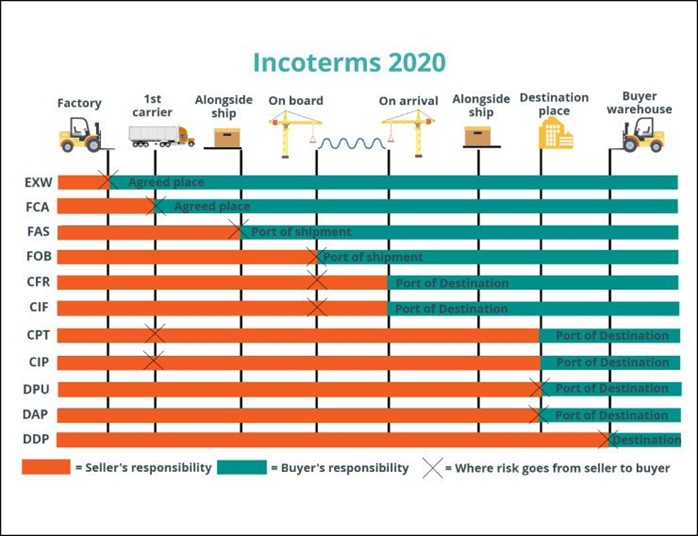
Incoterms 2020 includes 11 rules, which are grouped into two categories based on modes of transport:
- Any mode of transport: Seven rules apply to any mode of transport.
- Sea or land or inland waterway transport: Four rules apply to sea or land or inland waterway transport.
Some examples of Incoterms include:
- Cost, Insurance and Freight (CIF): The seller insures the goods up until they arrive at the port.
- Delivered at Place (DAP): The seller delivers the goods to an agreed location in the country of import.
- Delivered at Place Unloaded (DPU): The seller delivers and unloads the goods at the named place of destination.
- Free Alongside Ship (FAS): The seller delivers the goods right next to the ship at the destination stated in the contract.
You can find full details of all the Incoterms and their definitions on the International Chamber of Commerce website https://iccwbo.org/.
